It acts mainly by accelerating the rate of the neutralization of certain activated coagulation factors by antithrombin but other. Definition History Heparin.

Pdf Mechanisms Of Action Of Low Molecular Weight Heparins And Heparinoids Semantic Scholar
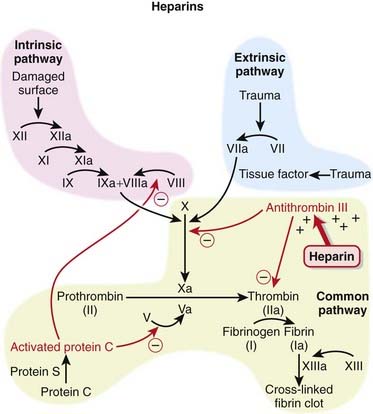
Potentiates the action of antithrombin III and thereby inactivates thrombin as well as other coagulation factors IXa Xa XIa XIIa and.
. Heparin also known as unfractionated heparin UFH is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Classification Uses Side Effects Heparin. This type of drug interferes with the bodys blood clotting process preventing blood clots from forming.
Heparin is a widely used injectable anticoagulant stops the formation of blood clots. These chains contain variable biological activity and molecular weight. Mode of action.
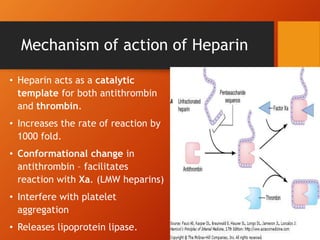
Heparin mechanism of action. Mechanism of Action. The mechanism of action of heparin is ATIII-dependent.
Unfractionated heparin UFH binds to anti-thrombin III AT-III which enhances antithrombins inhibition of several coagulation factors especially factor Xa and factor IIa. Mechanism of Action Heparin. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin they are considered.
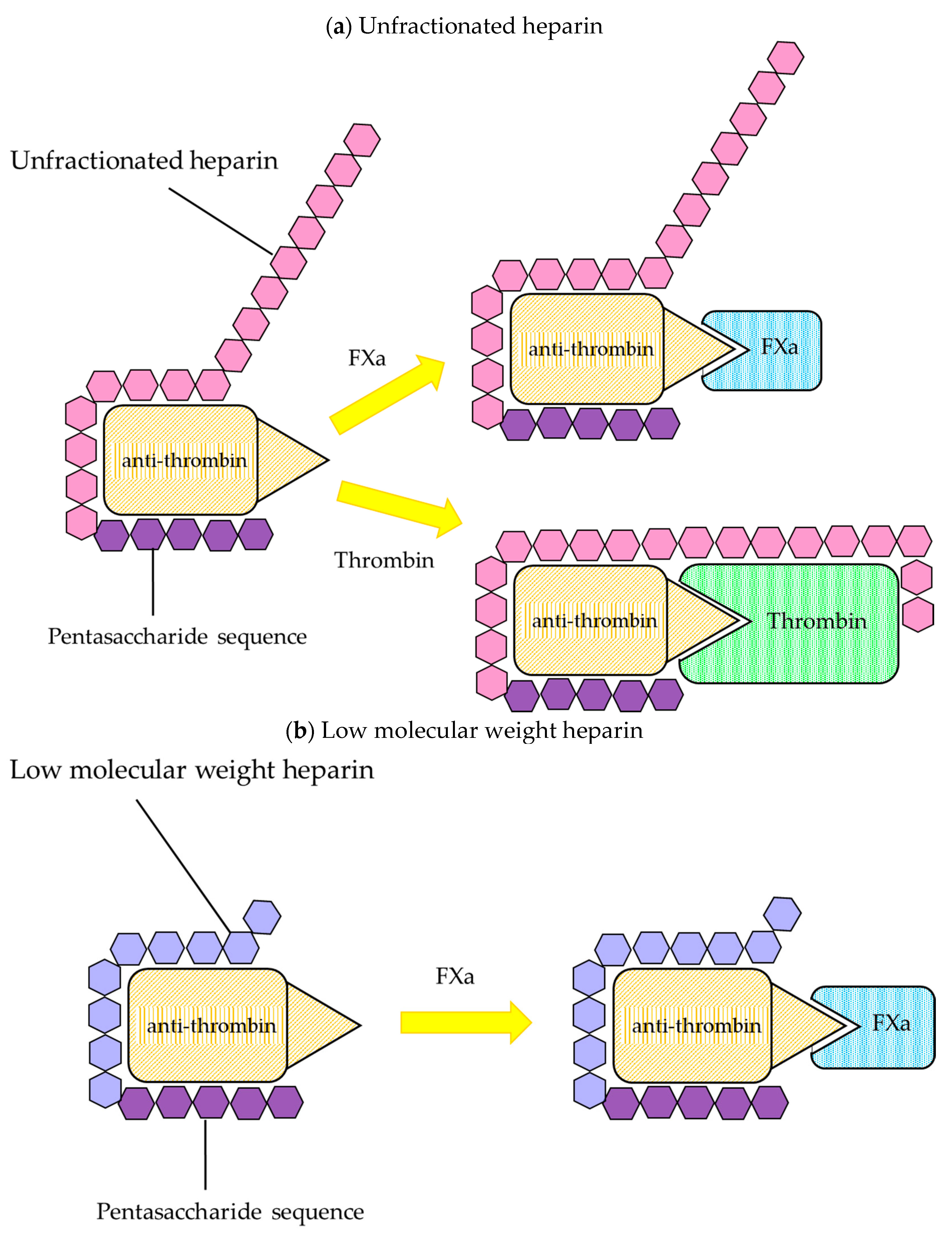
Heparin is administered in low. The original class Unfractionated Heparin UFH is a crude mixture of variable length polysaccharides derived from porcine intestinal mucosa. Heparin is a sulfated polysaccharide with a molecular weight range of 3000 to 30 000 Da mean 15 000.
Heparin inhibits coagulation by activating antithrombin III. What is heparin and how does it work mechanism of action. Mechanism of Action and Pharmacology of Unfractionated Heparin.
Mechanism of action pharmacokinetics dosing considerations monitoring efficacy and safety. Newer classes known as Low. However it is binding to an antithrombin that is important as this causes a surface change and.
Unfractionated heparin UFH is the outcome of a heterogeneous mixture of linear polysaccharide chains. This inhibits the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. Pharmacology Mechanism of Action.
Join us for our Pharmacology lecture on Heparin. During this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will guide you through the mechanism of action indications adverse drug reactions and. In particular heparin does not appear to have had a significant effect it is very important that a given assay procedure used on the reaction rates between antithrombin III and the in.
Heparin binds to antithrombin III to form a heparin-antithrombin III complex. Heparin is an anti-coagulant drug. Heparin is the anticoagulant of choice when a rapid anticoagulant effect is required because its onset of action is immediate when administered by IV injection.
The blood coagulation system is. Low-molecular-weight heparins LMWHs for example dalteparin enoxaparin among others are anticoagulants. Once administered heparin binds to several proteins.
Heparin works by activating antithrombin which is a naturally occurring protein in the bloodstream that prevents us from clotting too much. Coagulation cascade is a normal physiological process which aims at preventing. And fall in hematocrit or blood pressure.
These drugs are used in the prophylaxis of venous. Heparin is sometimes called a blood thinner but it. Low-molecular-weight heparin LMWH is a class of anticoagulant medications.
Heparin is the anticoagulant of choice when a rapid anticoagulant effect is required because its onset of action is immediate when administered by intravenous injection. Action Potentiates the inhibitory effect of antithrombin on factor Xa and thrombin. The complex binds to and.
The mechanism by which such high affinity heparin acts when antithrombin III is the inhibitor is promotion of the formation of an intermediate proteinase-heparin-antithrombin complex. Drug Interactions Contraindications Heparin. Heparin increases the inhibitory action of antithrombin III AT III on clotting factors XIIa XIa IXa Xa and thrombin.
Notify physician or nursing staff immediately if heparin.

Anticoagulants Heparin Osmosis

Lecture Notes On Anticoagulants Heparin Warfarin

Heparin Mechanisms Within The Coagulation Cascade Box A At Red Download Scientific Diagram

Mechanism Of Action Of Unfractionated And Low Molecular Weight Heparin Download Scientific Diagram
Biomedicines Free Full Text Updates On Anticoagulation And Laboratory Tools For Therapy Monitoring Of Heparin Vitamin K Antagonists And Direct Oral Anticoagulants Html

Heparin And Low Molecular Weight Heparin Mechanisms Of Action Pharmacokinetics Dosing Monitoring Efficacy And Safety Chest

Pharmacological And Clinical Application Of Heparin Progress An Essential Drug For Modern Medicine Sciencedirect

Heparin And Low Molecular Weight Heparin Mechanisms Of Action Pharmacokinetics Dosing Monitoring Efficacy And Safety Chest

Anticoagulants Hematology Medbullets Step 1

Mechanism Of Action Of Heparins And Fondaparinux Uptodate
Heparin Physiology Pharmacology And Clinical Application
Heparin Physiology Pharmacology And Clinical Application

Heparin Mechanism Of Action Youtube

Heparin Mechanism Of Action Study Com

Low Molecular Weight Heparins Nejm